Infrastructure as a Service
An IaaS cloud provider may supply users with a full variety of computing infrastructure, including storage, servers and networking gears as well as maintenance and support. Businesses may choose the computer resources they demand without having to deploy hardware on their premises. Some of the main IaaS cloud service providers are Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure and Google Compute Engine.
Key Features
- Instead of purchasing hardware completely, users pay for IaaS on demand
- Infrastructure is scalable depending on processing and storage needs.
- Saves enterprises the cost of buying and maintaining their hardware
- Because data is on the cloud, there can be no single point of failure.
- Enables the virtualization of administrative tasks, freeing up time for other work.
Benefits of IaaS
- Minimize costs - eliminates the need to deploy on-premises hardware, lowering expenses.
- Enhanced Scalability - enables to scale computing resources up or down based on demand.
- Simple Deployment - allows to quickly install servers, processing, storage and networking to get it up and running
Disadvantages of IaaS
- Management Complexity: Managing infrastructure in the cloud requires mastery in cloud technologies and architectures. Organizations might confront difficulties in successfully managing and advancing their cloud resources, including provisioning, monitoring, and troubleshooting.
- Dependency on Internet Connectivity: Since IaaS depends on internet availability to access and manage resources, organizations might encounter disturbances in services or execution issues assuming there are issues with their internet connections or the IaaS provider's network.
- Security Concerns: Storing sensitive data and running basic responsibilities in the cloud can raise security concerns. Organizations need to execute robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and consistence frameworks, to protect their data and infrastructure from cyber threats and breaks.
- Vendor Lock-In: Moving infrastructure and applications to a particular IaaS provider can bring about vendor lock-in, making it trying to switch providers or relocate to an alternate cloud environment later on. Organizations should to painstakingly consider their drawn out cloud system to moderate the risk of vendor lock-in.
- Cost Management: While IaaS offers cost efficiencies contrasted with conventional on-premises infrastructure, organizations need to carefully monitor and deal with their cloud spending to stay away from unexpected costs, without proper cost management practices, organizations might cause unnecessary costs, for example, overprovisioning resources or leaving unused resources running.
Platform as a Service
PaaS is simply a cloud basis where we can create, test and organize various apps for organization. Implementing PaaS streamlines the company's software development process. PaaS's virtual runtime environment provides a conducive environment for creating and testing applications.
Key Features
- PssS is a platform that includes tools for testing, developing and hosting applications all in the same environment.
- Allows enterprises to focus on development rather than underlying infrasturcture.
- Security, Operating Systems, Server Software, and backup are all managed by providers.
- Allows for collaborative work even when teams operate remotely.
Benefits of PaaS
- Minimal Development Time: decreases development time since the vendor supplies all computing resources such as server-side components, which streamlines the process and improves the development team's focus.
- Multiple Programming Language Support
- Enhanced Collaboration If the project involves several developers and vendors, PaaS is the best alternative because it rents all of the necessary computing and networking resources.
Disadvantages of PaaS
- Limited Customization
- Less control over data processing
- Learning Curve
Software as a Service
SaaS is a business model that provides instant access to cloud-based online applications The vendor is in charge of the complete computer stack, which may be accessed via a web browser. These programs are hosted in the cloud and may be accessed via a paid licenced subscription or free with limited access. SaaS does not necessiate any installs or downloads to local computer infrastructure. Examples include Google G Suite, Microsoft Office 365, Dropbox etc.
Key Features
- Software and apps are delivered to consumers via a subscription model by SaaS Companies.
- Users are not required to manage, install or upgrade software; this is handled by SaaS providers.
- Data is secure in the cloud; failure of equipment does not result in data loss.
- Resource use may be scaled based on service requirements.
- Applications may be accessed from practically any internet-connected device, anywhere in the globe.
Benefits of SaaS
- Affordable: SaaS is cost-effective because it reduces the costs associated with purchasing, installing, maintaining, and upgrading computer hardware.
- Accessibility from Anywhere: using any device, removing the limits imposed by on-premises software.
- Ready to use: Users only need to sign up for the service to have access to quick and powerful computing resources.
Disadvantages of SaaS
- Users have no control over the hardware assigned because only seller can handle the software.
- Dependency on internet connectivity.
- Vendor lock in
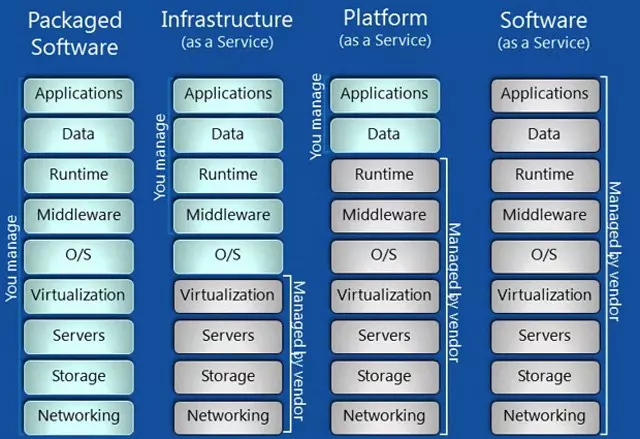
Fig: Differences between Packaged Software, IaaS, PaaS, SaaS in context to who manages the components.
Comparison of Cloud Service Models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
| Feature | Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) | Platform as a Service (PaaS) | Software as a Service (SaaS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Provides virtualized computing resources like servers, storage, and networking. | Offers a platform with tools and environments for application development. | Delivers ready-to-use software applications over the internet. |
| Control Level | High: Users manage OS, middleware, apps, and data. | Medium: Users control apps and data; the provider manages infrastructure. | Low: Users only manage software configuration and usage. |
| Examples | AWS EC2, Microsoft Azure VM, Google Compute Engine. | AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, Heroku. | Google Workspace, Salesforce, Dropbox. |
| Target Users | IT administrators and developers requiring full control of infrastructure. | Developers looking for a managed platform to build and deploy applications. | End-users needing ready-to-use applications without technical expertise. |
| Use Cases | Hosting websites, storage, disaster recovery, and virtual machines. | Software development, app testing, and deployment. | Email, CRM, file sharing, and collaboration tools. |
| Infrastructure Access | Provides direct access to virtualized hardware. | Abstracts the infrastructure, offering tools and frameworks. | No access to underlying infrastructure. |
Cloud Design and Implementation Using SOA
Service Oriented Architecture (SOA)
A service-oriented architecture (SOA) is a design paradigm that creates or supplements applications with self-contained, reusable building blocks—services—that provide specific functions and can be invoked over a network. Each service has a defined scope and can be accessed by other components or services within the architecture to enhance the overall functionality and performance of the system. Examples of services in a SOA include a payment processing service, a customer management service, or a product recommendation service that can be embedded in an ecommerce site. SOA makes for a modular and flexible software infrastructure, where individual services can be developed, tested, and deployed independently. Two key benefits are ease of maintenance and scalability. SOA works by loosely coupling services within the framework of an application. Each service works as a module capable of delivering the input/output requested. The application doesn't need to know the version of the service it's using. Instead, it checks a registry and finds the most current service offering the functionality needed.
Key steps in designing and implementing a cloud solution using SOA
- Identify service boundaries
- Analyze the system requirements and identify logical boundaries for diffreent services.
- Define responsibilities and scope of each service.
- Define service contracts
- Specify the interfaces and contracts for each service, including message formats, protocols, and Service-Level Aggrements (SLAs).
- Implement services
- Services can be implemented using various technologies and languages such as RESTful APIs, SOAP or microservices.
- Deploy services in the cloud.
- Choose a cloud platform that supports our service deployment requirements. Platforms like AWS, Azure etc.
- Implement service governance
- Establish policies and procedures for managing the lifecycle of services.
- Implement service composition
- COmpose services to create larger business processes or applications
- Monitor and manage services
- Implement monitoring and management tools to track the performance, availability and usage of deployed services.
Security, Trust and Privacy
Security
Security is defined as the preservation of information, confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Other attributes such as authenticity, accountability, non-repudiation, and dependability may also be included.
Confidentiality is a security feature that ensures information is not made available or given to unauthorized people, companies, or processes.
The total correctness, completeness, and consistency of data entities or processes throughout its lifecycle is referred to as integrity.
The process of ensuring that data is available to end-users and applications when they need it is known as availability.
Security is one of the most fundamental foundations of privacy. Any entity that creates, maintains, uses, or disseminates data must guarantee that these records have not been tampered with and must take on safeguards to prevent the information from being misused. To be more specific, to maintain the security of such information processing, data controllers must establish suitable technological and organizational safeguards to protect it against unauthorized access or disclosure, destruction, modification, and unauthorized use. Mechanisms for doing this include risk assessment, implementation of an information security program, and the implementation of effective, reasonable, and appropriate measures covering physical, administrative, and technological components of security.
Key aspects of security are: Data encryption, Identity and access management, Vulnerability management, Data backup and recovery.
Trust
Trust refers to the confidence, reliance, and belief that one person or entity has in another person or organization. Trust in cloud computing refers to the confidence, reliance, and belief towards cloud services and its infrastructures. Trust is a broader notion that than security that involves human psychology, brand loyalty, and friendliness. Establishing trust is essential to encourage the adoption and utilization of cloud services.
Key factors that contribute to trust include security measures, data privacy, service reliability and availability, data ownership and control, etc.
Privacy
Privacy is the ability to keep information and activities confidential and protected from unauthorized access. It encompasses the right to control and manage one's personal data, communications, and online presence. Privacy in cloud computing refers to the protection and control of personal and sensitive data stored, processed, and transmitted through cloud services. It is important for users to assess the privacy practices and capabilities of cloud service providers.
Some key aspects to consider regarding privacy are data confidentiality, data ownership and control, transparency and auditing, data breach response, regulatory compliance, etc.
Cloud Computing Reference Model (General Architecture)
The cloud computing reference model is a general high-level architecture and is meant to aid understanding of the cloud computing needs, uses, features, and standards. This architecture is an overview of the NIST cloud computing reference architecture, which outlines the primary actor and their cloud computing activities and roles.

The NIST cloud computing reference architecture identifies five primary players.
-
Cloud consumer
A cloud consumer is a person or organization who has a commercial connection with a cloud provider and consumes its services. A cloud consumer browses and uses a cloud provider's service and makes payments appropriately.
-
Cloud provider.
A cloud provider is a person or an organization that is responsible for making a service available to interested parties. Cloud provider deploys, configures, maintains, and upgrades the cloud software and infrastructure.
-
Cloud auditor.
A cloud auditor is a party who can do analysis of cloud service controls to provide an opinion on them. Audits are carried out to ensure that standards are met in terms of security measures, performance, privacy, etc.
-
Cloud broker.
A cloud broker is a company that handles the usage, performance, and delivery of cloud services and negotiates contracts between cloud providers and cloud users.
-
Cloud carrier.
A cloud carrier operates as a middleman between cloud users and cloud providers, providing connectivity and transfers of cloud services. Cloud carriers give users access via a network access devices such as PCs, Laptops, Mobile Phones, etc.